Ontologies of research areas have been proven to be useful in many application for analysing and making sense of scholarly data. In this lecture, I will present how we produced the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), which is the largest ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science, and discuss a number of applications that build on CSO, to support high-level tasks, such as topic classification, research trends forecasting, metadata extraction, and recommendation of books.
Tag: Ontology Learning
Ontology Extraction and Usage in the Scholarly Knowledge Domain
Ontologies of research areas have been proven to be useful in many application for analysing and making sense of scholarly data. In this chapter, we present the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), which is the largest ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science, and discuss a number of applications that build on CSO, to support high-level tasks, such as topic classification, metadata extraction, and recommendation of books.

The Computer Science Ontology: A Comprehensive Automatically-Generated Taxonomy of Research Areas
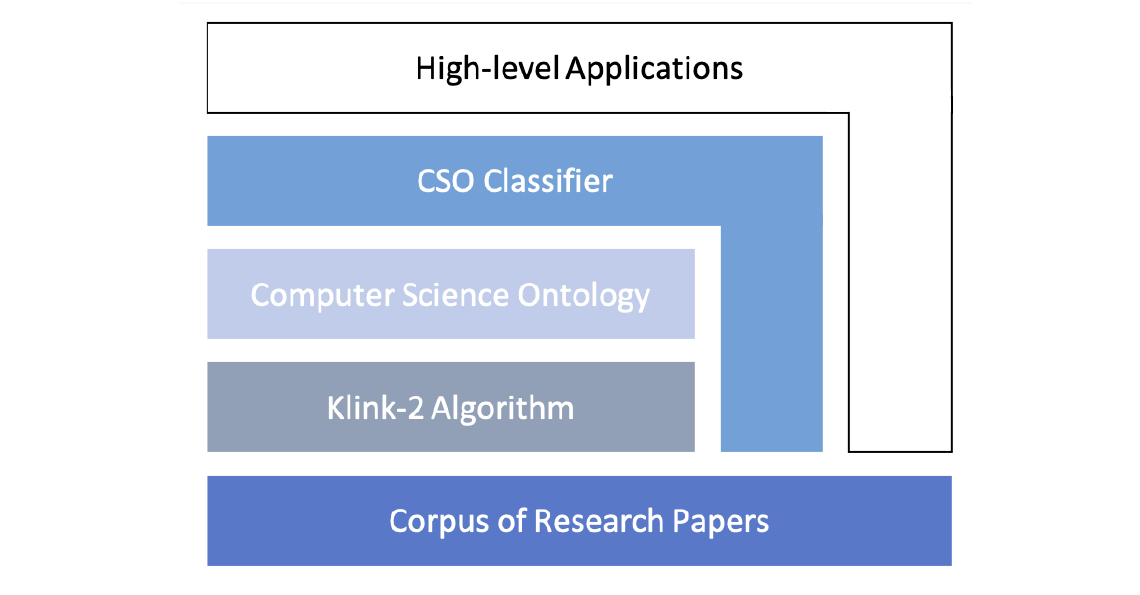
Ontologies of research areas are important tools for characterising, exploring, and analysing the research landscape. Some fields of research are comprehensively described by large-scale taxonomies, e.g., MeSH in Biology and PhySH in Physics. Conversely, current Computer Science taxonomies are coarse-grained and tend to evolve slowly. For instance, the ACM classification scheme contains only about 2K research topics and the last version dates back to 2012. In this paper, we introduce the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a large-scale, automatically generated ontology of research areas, which includes about 14K topics and 162K semantic relationships. It was created by applying the Klink-2 algorithm on a very large dataset of 16M scientific articles. CSO presents two main advantages over the alternatives: i) it includes a very large number of topics that do not appear in other classifications, and ii) it can be updated automatically by running Klink-2 on recent corpora of publications. CSO powers several tools adopted by the editorial team at Springer Nature and has been used to enable a variety of solutions, such as classifying research publications, detecting research communities, and predicting research trends. To facilitate the uptake of CSO, we have also released the CSO Classifier, a tool for automatically classifying research papers, and the CSO Portal, a web application that enables users to download, explore, and provide granular feedback on CSO. Users can use the portal to navigate and visualise sections of the ontology, rate topics and relationships, and suggest missing ones. The portal will support the publication of and access to regular new releases of CSO, with the aim of providing a comprehensive resource to the various research communities engaged with scholarly data.
New release: CSO Classifier v2.1
We are pleased to announce that we recently created a new release of the CSO Classifier (v2.1), an application for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO). Recently, we have been intensively working on improving its scalability, removing all its bottlenecks and making sure it could be run on large corpus. […]

CSO Classifier
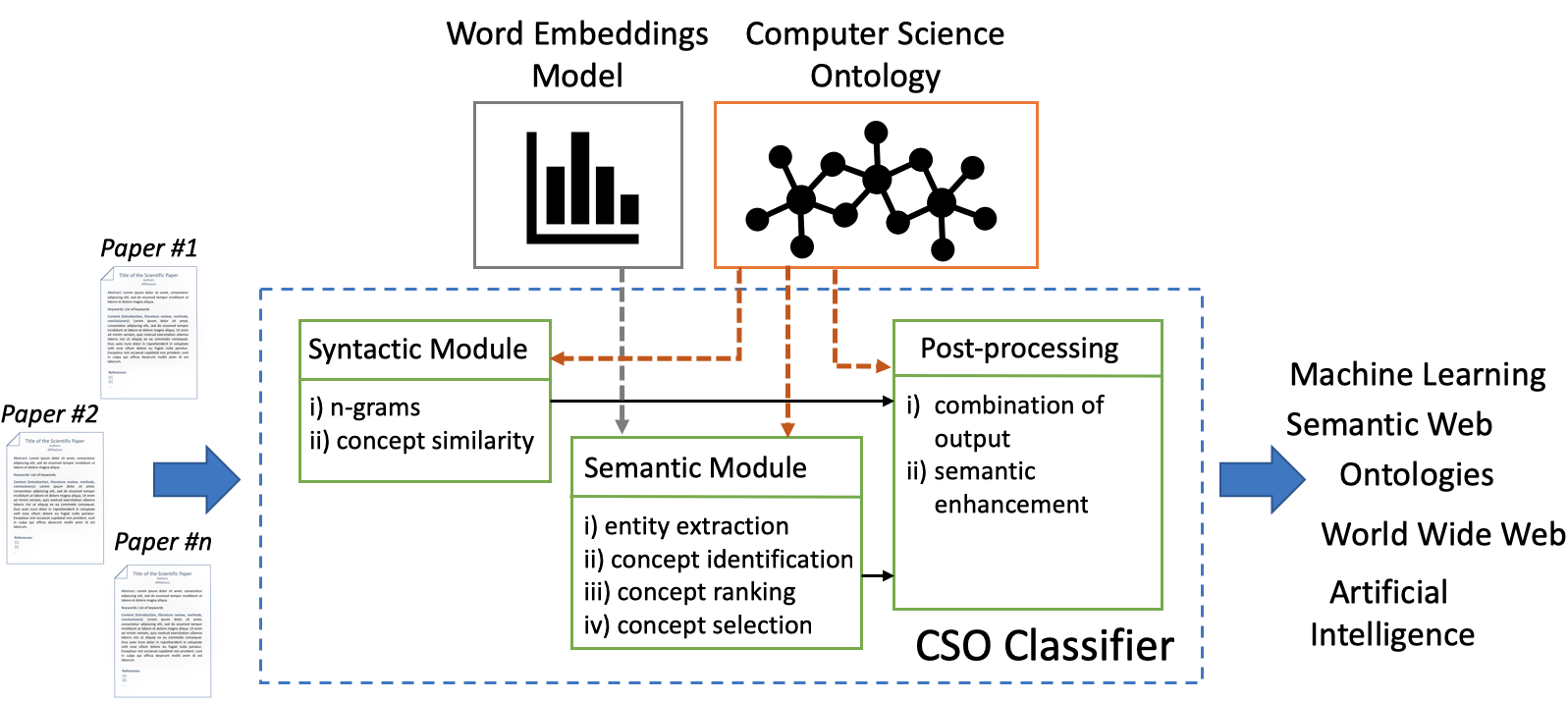
Classifying research papers according to their research topics is an important task to improve their retrievability, assist the creation of smart analytics, and support a variety of approaches for analysing and making sense of the research environment. In this page, we present the CSO Classifier, a new unsupervised approach for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a comprehensive ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science.
Computer Science Ontology
The Computer Science Ontology is a large-scale ontology of research areas that was automatically generated using the Klink-2 algorithm on a dataset of about 16 million publications, mainly in the field of Computer Science. In the rest of the paper, we will refer to this corpus as the Rexplore dataset.
The current version of CSO includes 14,164 topics and 162,121 semantic relationships. The main root is Computer Science; however, the ontology includes also a few secondary roots, such as Linguistics, Geometry, Semantics, and so on.
CSO presents two main advantages over manually crafted categorisations used in Computer Science (e.g., 2012 ACM Classification, Microsoft Academic Search Classification). First, it can characterise higher-level research areas by means of hundreds of sub-topics and related terms, which enables to map very specific terms to higher-level research areas. Secondly, it can be easily updated by running Klink-2 on a set of new publications.

Classifying Research Papers with the Computer Science Ontology
The CSO Classifier is an application for automatically classifying academic papers according to the rich taxonomy of topics from CSO. The aim is to facilitate the adoption of CSO across the various communities engaged with scholarly data and to foster the development of new applications based on this knowledge base.
Supporting Springer Nature Editors by means of Semantic Technologies
“Supporting Springer Nature Editors by means of Semantic Technologies” is a research paper accepted to the Industry Track at the International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC) 2017 , 21-25 October 2017, Vienna, Austria. Authors Francesco Osborne, Angelo Salatino, Thiviyan Thanapalasingam, Aliaksandr Birukou and Enrico Motta Abstract The Open University and Springer Nature have been collaborating since 2015 […]
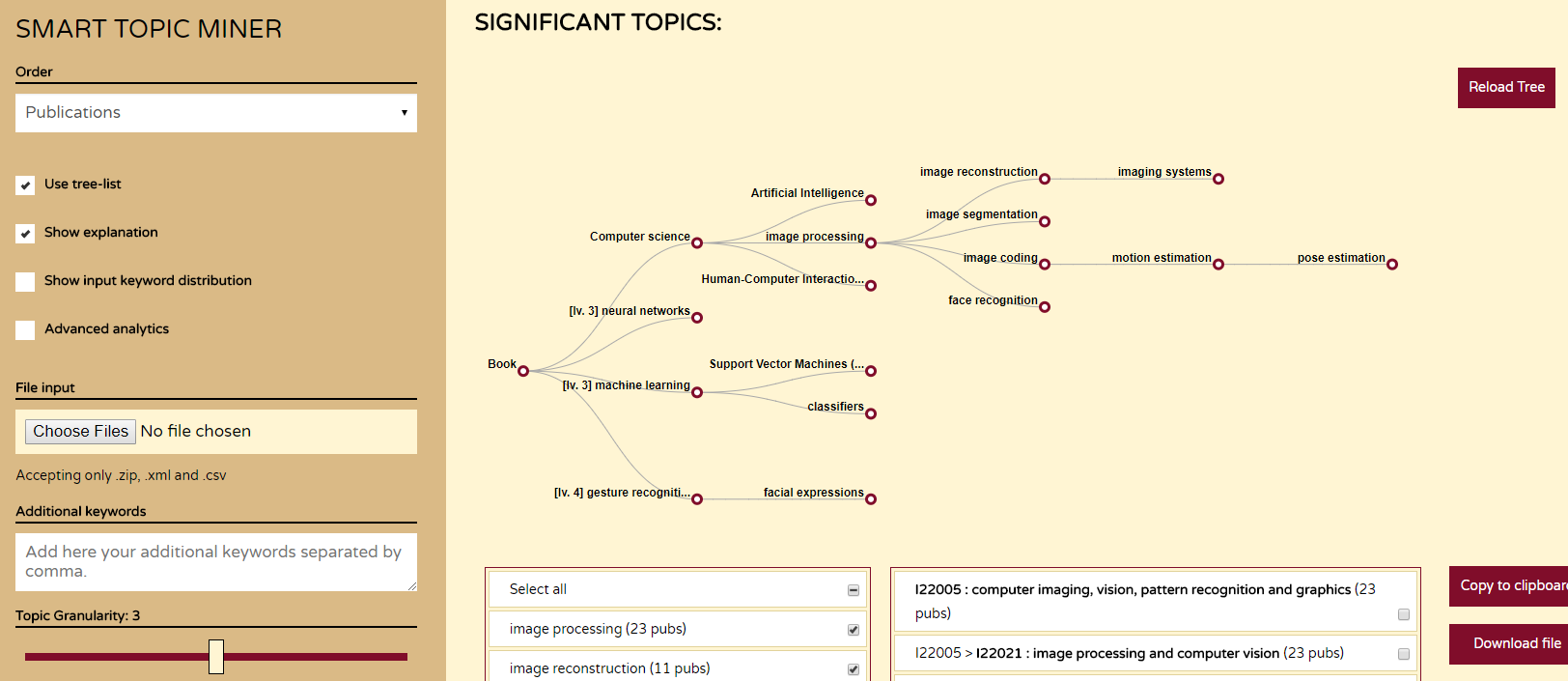
Smart Topic Miner: Supporting Springer Nature Editors with Semantic Web Technologies
“Smart Topic Miner: Supporting Springer Nature Editors with Semantic Web Technologies” is poster paper presented at the Poster and Demo session [D45] on Wednesday 19th October 2016 at the 15th International Semantic Web Conference in Kobe, Japan Authors: Francesco Osborne, Angelo Antonio Salatino, Aliaksandr Birukou and Enrico Motta Abstract: Academic publishers, such as Springer Nature, annotate scholarly products […]
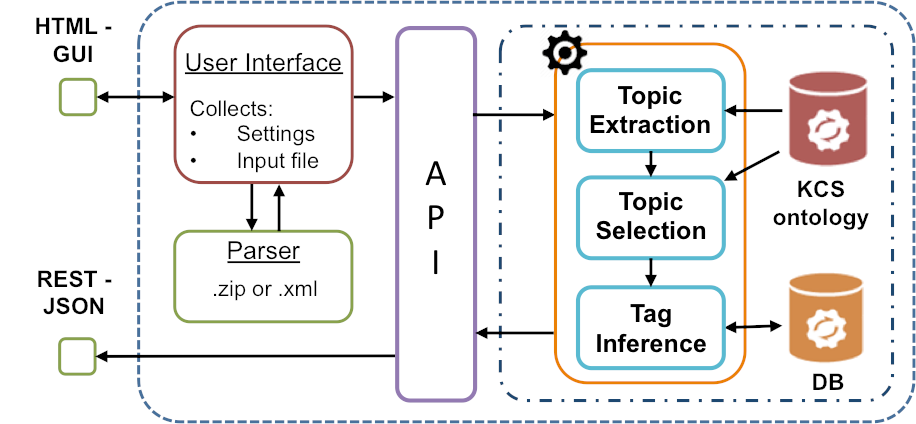
Automatic Classification of Springer Nature Proceedings with Smart Topic Miner
“Automatic Classification of Springer Nature Proceedings with Smart Topic Miner” is conference paper presented on Friday 21st October 2016 at the 15th International Semantic Web Conference in Kobe, Japan Authors: Francesco Osborne, Angelo Antonio Salatino, Aliaksandr Birukou and Enrico Motta Abstract: The process of classifying scholarly outputs is crucial to ensure timely access to knowledge. However, this […]



