“Characterising Research Areas in the field of AI” is a research paper submitted to the special track “Statistical Methods for Science Mapping” on “51st Scientific Meeting of the Italian Statistical Society”. Alessandra Belfiore1, Angelo Salatino2, Francesco Osborne2 1 Università della Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Caserta (Italy) 2 Knowledge Media Institute, The Open University, Milton Keynes (UK) Abstract […]
Category: R
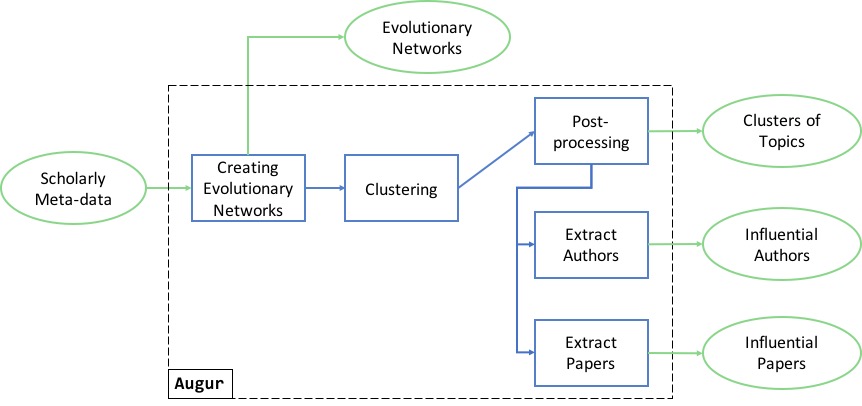
AUGUR: Forecasting the Emergence of New Research Topics
“AUGUR: Forecasting the Emergence of New Research Topics” is a paper submitted to the ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2018, presented on June 5 2018, in Fort Worth, TX, USA Angelo Salatino, Francesco Osborne and Enrico Motta Abstract Being able to rapidly recognise new research trends is strategic for many stakeholders, including universities, […]
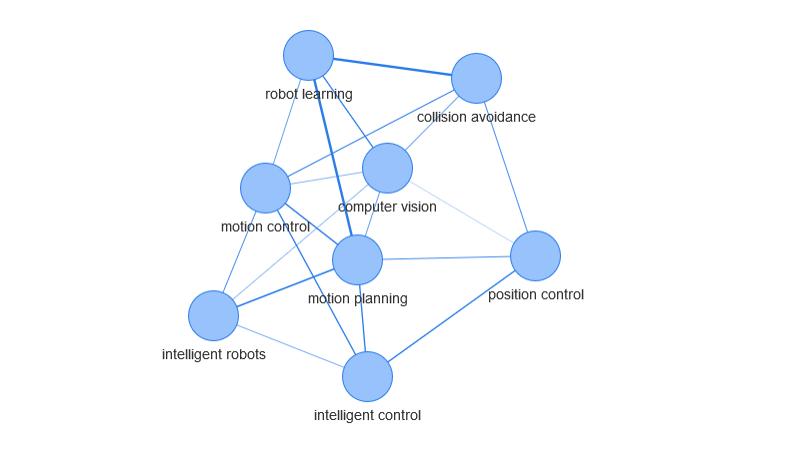
Export Graph in R via JSON
This post presents an easy solution for exporting and importing a graph object of igraph library. In its previous versions, the library used to have the save and load functions in which you could respectively export and import the graph object [1]. Although they seem to not be in the library anymore, the documentation states: “Attribute values […]
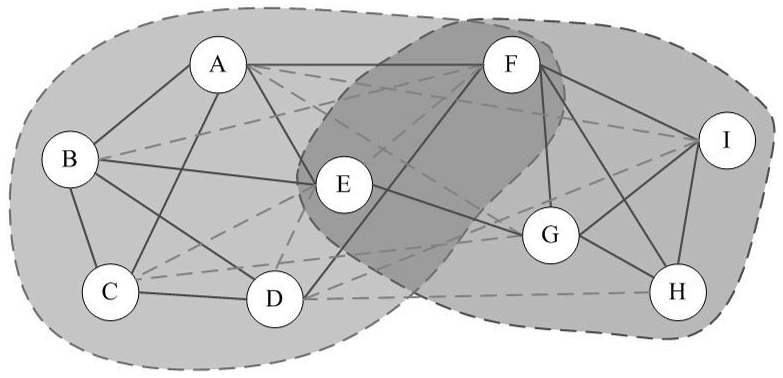
Clique Percolation Method in R: a fast implementation
Clique Percolation Method (CPM) is an algorithm for finding overlapping communities within networks, introduced by Palla et al. (2005, see references). This implementation in R, firstly detects communities of size k, then creates a clique graph. Each community will be represented by each connected component in the clique graph. Algorithm The algorithm performs the following […]
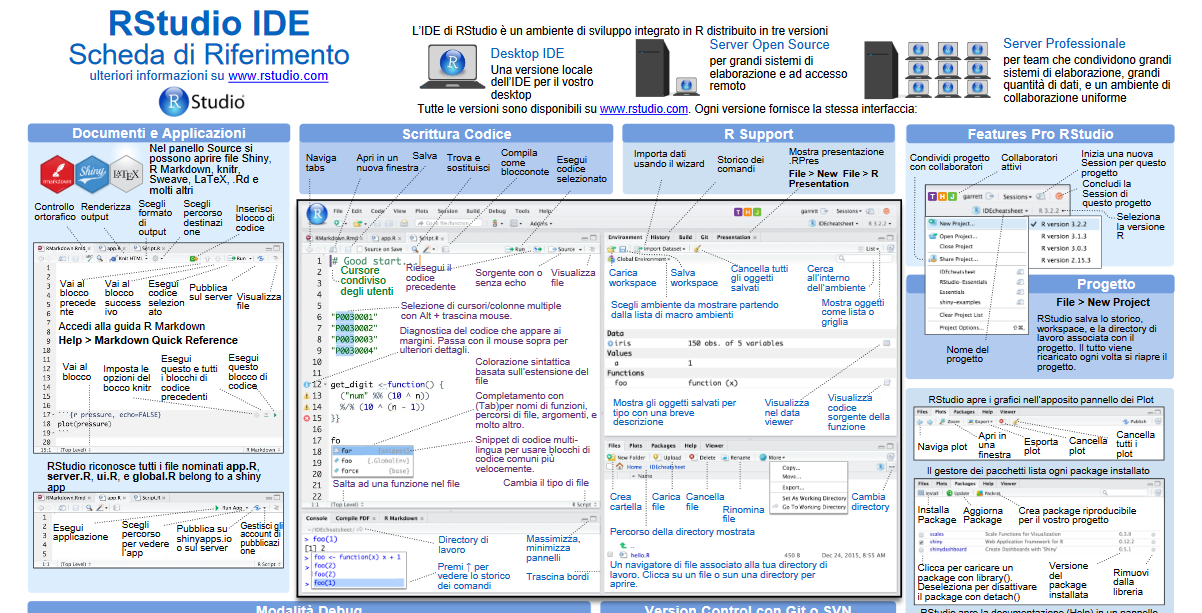
Italian translation of official RStudio cheatsheets
I recently joined the community of RStudio, which is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for R (an open source statistical language to make sense of data). My contribution is providing the Italian Translation of their cheatsheet (Schede di Riferimento).



