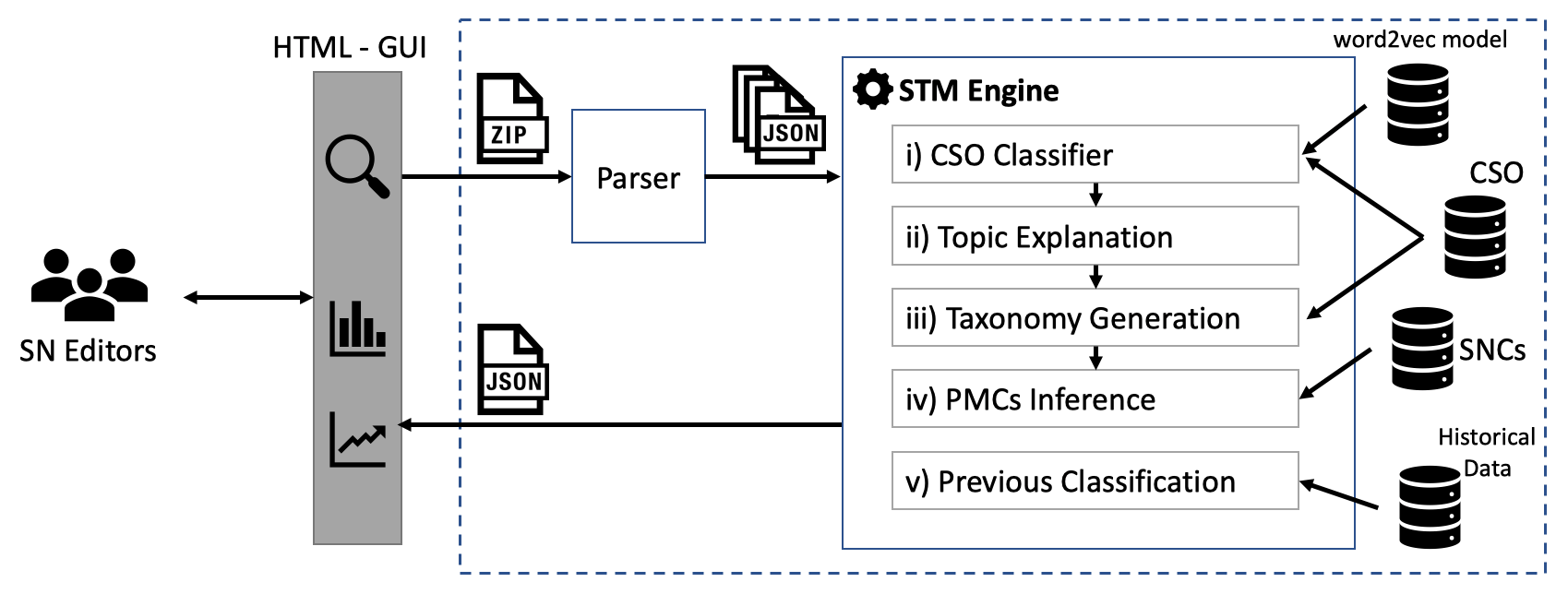
Identifying the research topics that best describe the scope of a scientific publication is a crucial task for editors, in particular because the quality of these annotations determine how effectively users are able to discover the right content in online libraries. For this reason, Springer Nature, the world’s largest academic book publisher, has traditionally entrusted this task to their most expert editors. These editors manually analyse all new books, possibly including hundreds of chapters, and produce a list of the most relevant topics. Hence, this process has traditionally been very expensive, time-consuming, and confined to a few senior editors. For these reasons, back in 2016 we developed Smart Topic Miner (STM), an ontology-driven application that assists the Springer Nature editorial team in annotating the volumes of all books covering conference proceedings in Computer Science. Since then STM has been regularly used by editors in Germany, China, Brazil, India, and Japan, for a total of about 800 volumes per year. Over the past three years the initial prototype has iteratively evolved in response to feedback from the users and evolving requirements.
Category: Web Technologies

The CSO Classifier: Ontology-Driven Detection of Research Topics in Scholarly Articles
Classifying research papers according to their research topics is an important task to improve their retrievability, assist the creation of smart analytics, and support a variety of approaches for analysing and making sense of the research environment. In this paper, we present the CSO Classifier, a new unsupervised approach for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a comprehensive ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science. The CSO Classifier takes as input the metadata associated with a research paper (title, abstract, keywords) and returns a selection of research concepts drawn from the ontology. The approach was evaluated on a gold standard of manually annotated articles yielding a significant improvement over alternative methods.

CSO Classifier
Classifying research papers according to their research topics is an important task to improve their retrievability, assist the creation of smart analytics, and support a variety of approaches for analysing and making sense of the research environment. In this page, we present the CSO Classifier, a new unsupervised approach for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a comprehensive ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science.

The World Wide Web turns 30
I have always been passionate about technology. When I bought my first computer (special thanks to my father for funding it), and got it connected to the internet, it soon became part of my life: downloading movies, music, studying, chatting, engaging with different communities, writing a blog, buying and selling stuff. The web gave me […]
Awesome Scholarly Data Analysis
Awesome Scholarly Data Analysis is a curated collection of resources that can support Scholarly Data analytics. This list ranges from: Datasets, which includes different corpora of papers, citations, authors and others, as well as taxonomies and ontologies of research concepts; Tools for collecting and classifying research papers, information extraction, and visualization; and Venues, Summer Schools, […]
Computer Science Ontology
The Computer Science Ontology is a large-scale ontology of research areas that was automatically generated using the Klink-2 algorithm on a dataset of about 16 million publications, mainly in the field of Computer Science. In the rest of the paper, we will refer to this corpus as the Rexplore dataset.
The current version of CSO includes 14,164 topics and 162,121 semantic relationships. The main root is Computer Science; however, the ontology includes also a few secondary roots, such as Linguistics, Geometry, Semantics, and so on.
CSO presents two main advantages over manually crafted categorisations used in Computer Science (e.g., 2012 ACM Classification, Microsoft Academic Search Classification). First, it can characterise higher-level research areas by means of hundreds of sub-topics and related terms, which enables to map very specific terms to higher-level research areas. Secondly, it can be easily updated by running Klink-2 on a set of new publications.

Classifying Research Papers with the Computer Science Ontology
The CSO Classifier is an application for automatically classifying academic papers according to the rich taxonomy of topics from CSO. The aim is to facilitate the adoption of CSO across the various communities engaged with scholarly data and to foster the development of new applications based on this knowledge base.
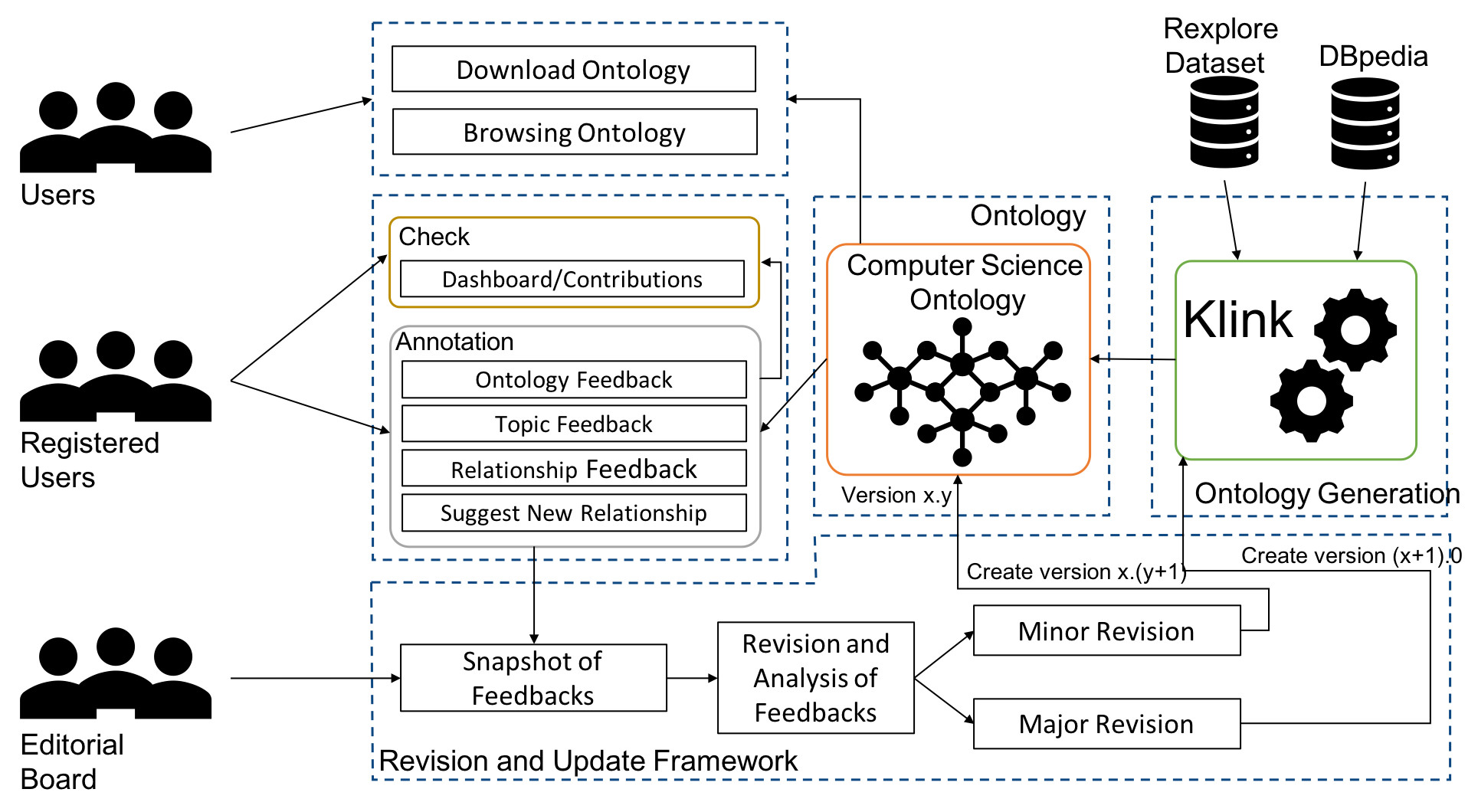
The Computer Science Ontology: A Large-Scale Taxonomy of Research Areas
Ontologies of research areas are important tools for characterising, exploring, and analysing the research landscape. Some fields of research are comprehensively described by large-scale taxonomies, e.g., MeSH in Biology and PhySH in Physics. Conversely, current Computer Science taxonomies are coarse-grained and tend to evolve slowly. For instance, the ACM classification scheme contains only about 2K research topics and the last version dates back to 2012. In this paper, we introduce the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a large-scale, automatically generated ontology of research areas, which includes about 26K topics and 226K semantic relationships. It was created by applying the Klink-2 algorithm on a very large dataset of 16M scientific articles.

Supporting Editorial Activities at Springer Nature
The project aims at fostering Springer Nature editorial activities by supporting them with a variety of smart solutions leveraging artificial intelligence, data mining, and semantic technologies. In particular, the KMi team will support Springer Nature editorial team in classifying proceedings and other editorial products, taking informed decisions about their marketing strategy, and improve their internal classification.
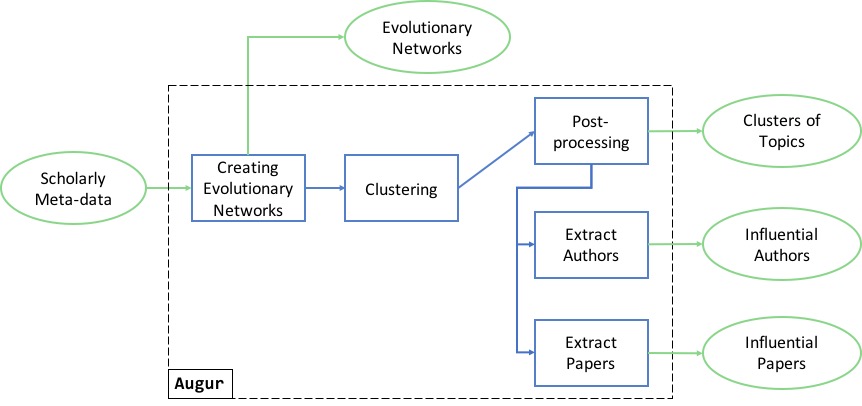
AUGUR: Forecasting the Emergence of New Research Topics
“AUGUR: Forecasting the Emergence of New Research Topics” is a paper submitted to the ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2018, presented on June 5 2018, in Fort Worth, TX, USA Angelo Salatino, Francesco Osborne and Enrico Motta Abstract Being able to rapidly recognise new research trends is strategic for many stakeholders, including universities, […]