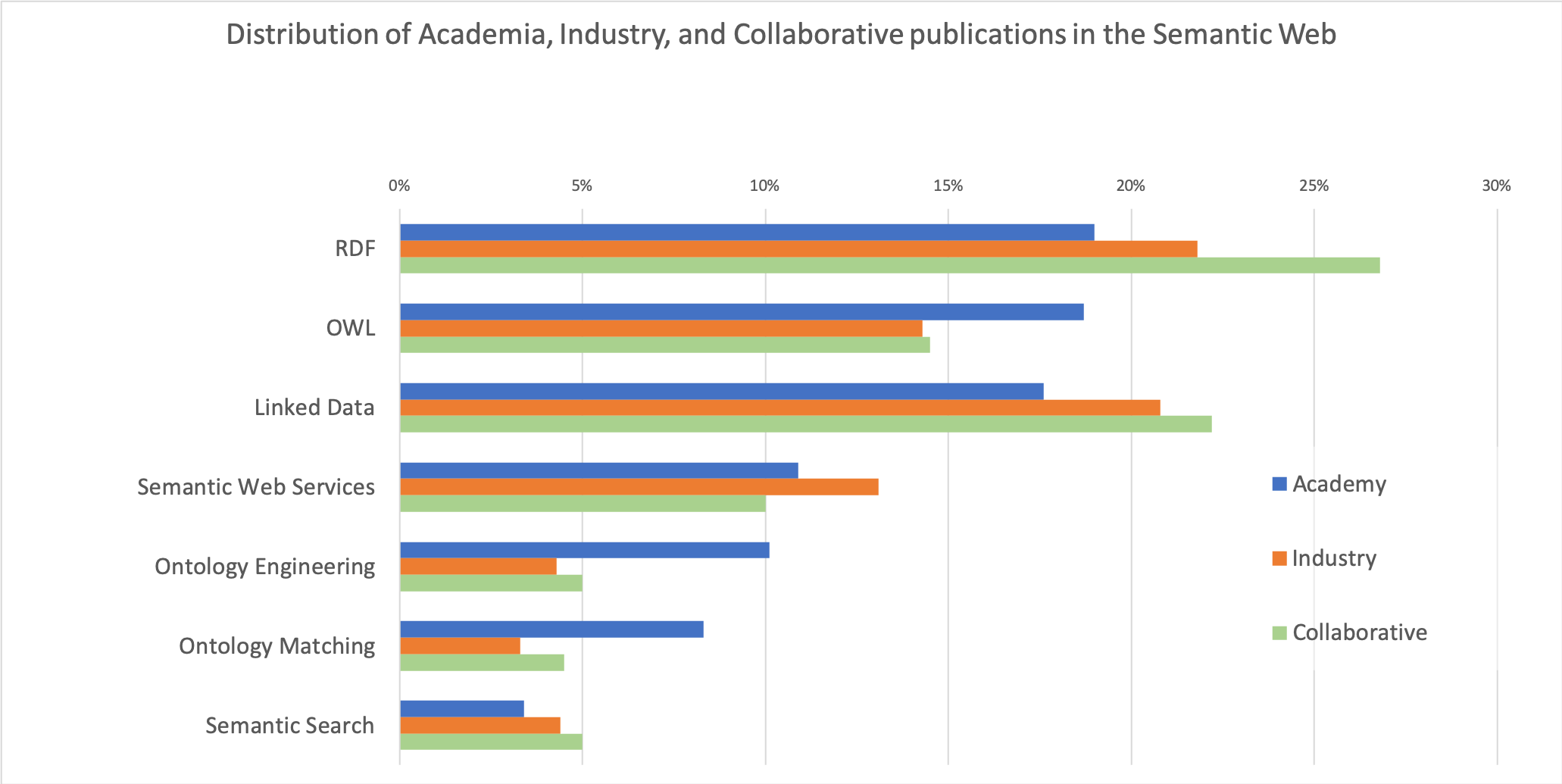
Analysing the relationship between academia and industry allows us to understand how the knowledge produced by the universities is being adopted and enriched by the industrial sector, and ultimately affects society through the release of relevant products and services. In this paper, we present a preliminary approach to assess and compare the research outputs of academia and industry. This solution integrates data from several knowledge graphs describing scientific articles (Microsoft Academics Graph), research topics (Computer Science Ontology), organizations (Global Research Identifier Database), and types of industry (DBpedia). We focus on the Semantic Web as exemplary field and report several insights regarding the different behaviours of academia and industry, and the types of industries most active in this field.
Category: Data Mining
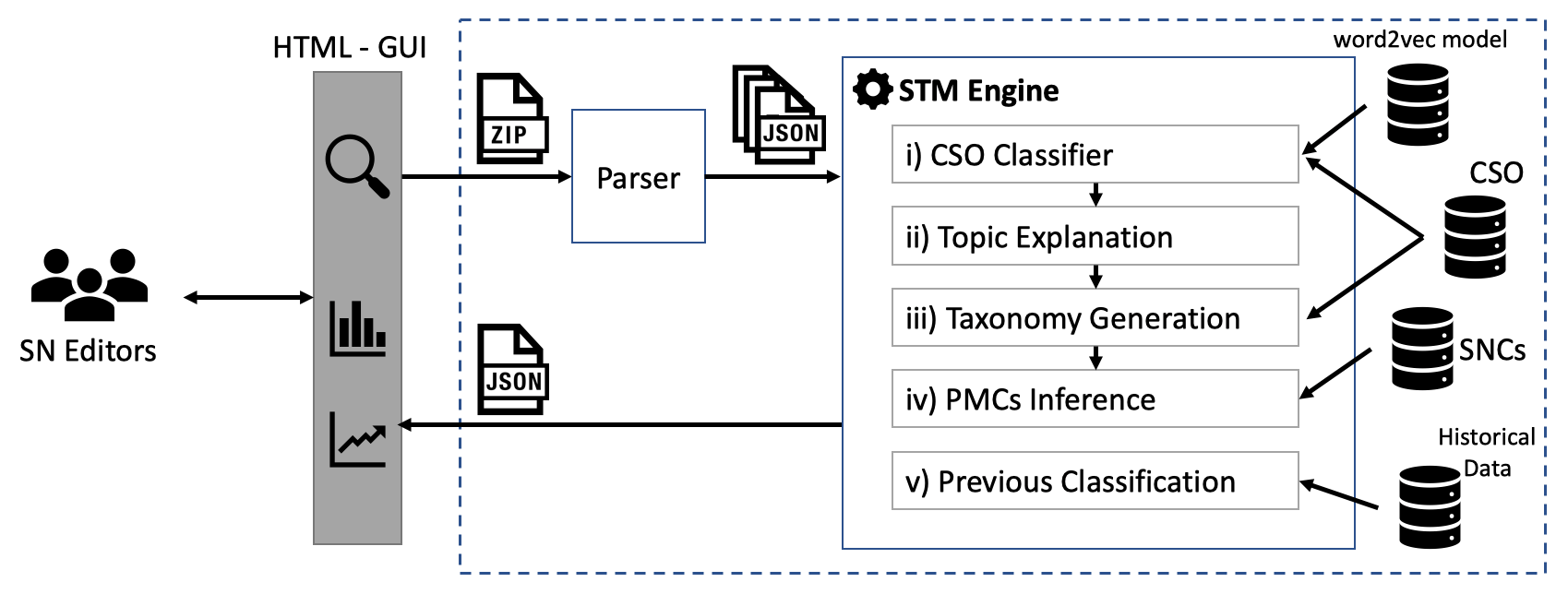
Improving Editorial Workflow and Metadata Quality at Springer Nature
Identifying the research topics that best describe the scope of a scientific publication is a crucial task for editors, in particular because the quality of these annotations determine how effectively users are able to discover the right content in online libraries. For this reason, Springer Nature, the world’s largest academic book publisher, has traditionally entrusted this task to their most expert editors. These editors manually analyse all new books, possibly including hundreds of chapters, and produce a list of the most relevant topics. Hence, this process has traditionally been very expensive, time-consuming, and confined to a few senior editors. For these reasons, back in 2016 we developed Smart Topic Miner (STM), an ontology-driven application that assists the Springer Nature editorial team in annotating the volumes of all books covering conference proceedings in Computer Science. Since then STM has been regularly used by editors in Germany, China, Brazil, India, and Japan, for a total of about 800 volumes per year. Over the past three years the initial prototype has iteratively evolved in response to feedback from the users and evolving requirements.

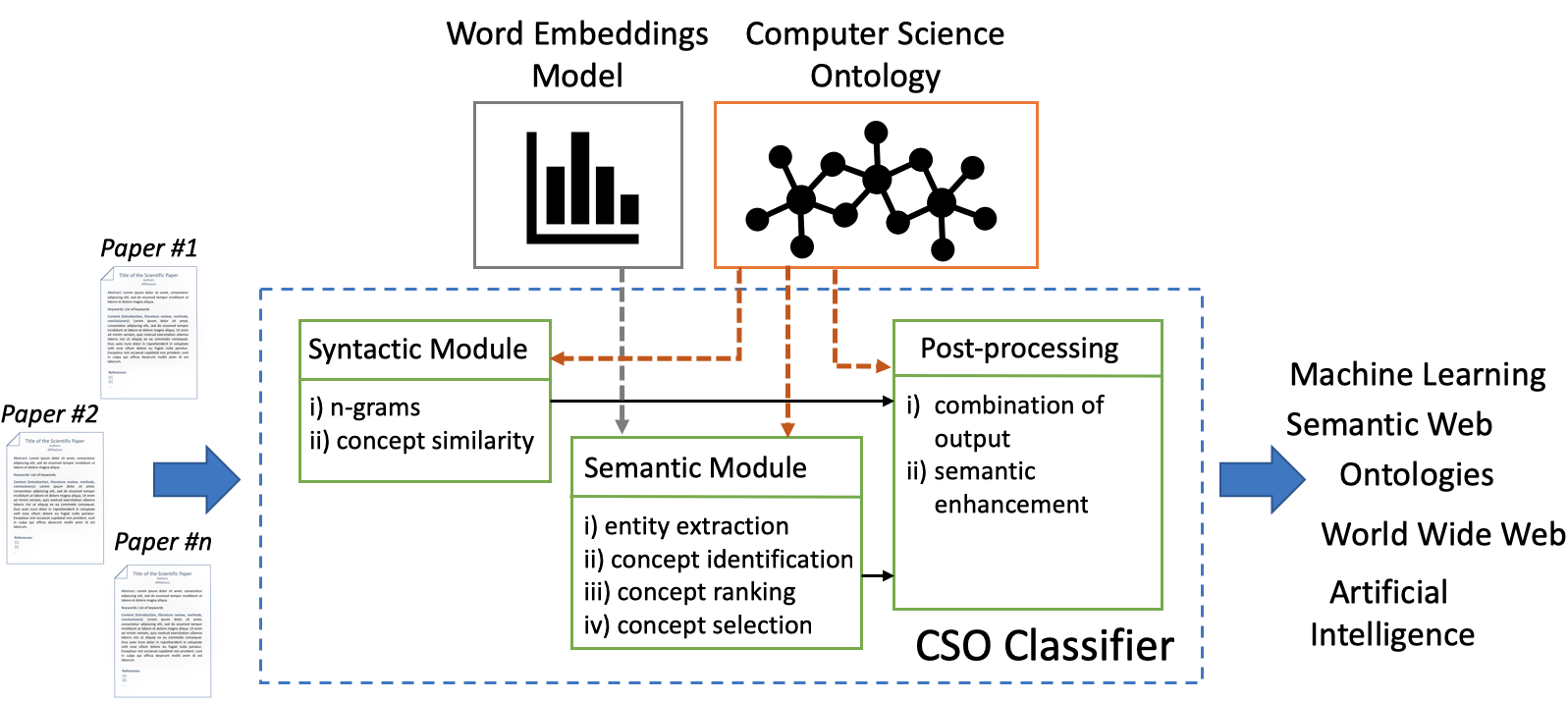
The CSO Classifier: Ontology-Driven Detection of Research Topics in Scholarly Articles
Classifying research papers according to their research topics is an important task to improve their retrievability, assist the creation of smart analytics, and support a variety of approaches for analysing and making sense of the research environment. In this paper, we present the CSO Classifier, a new unsupervised approach for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a comprehensive ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science. The CSO Classifier takes as input the metadata associated with a research paper (title, abstract, keywords) and returns a selection of research concepts drawn from the ontology. The approach was evaluated on a gold standard of manually annotated articles yielding a significant improvement over alternative methods.
New release: CSO Classifier v2.1
We are pleased to announce that we recently created a new release of the CSO Classifier (v2.1), an application for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO). Recently, we have been intensively working on improving its scalability, removing all its bottlenecks and making sure it could be run on large corpus. […]

CSO Classifier
Classifying research papers according to their research topics is an important task to improve their retrievability, assist the creation of smart analytics, and support a variety of approaches for analysing and making sense of the research environment. In this page, we present the CSO Classifier, a new unsupervised approach for automatically classifying research papers according to the Computer Science Ontology (CSO), a comprehensive ontology of research areas in the field of Computer Science.

Invited Talk – Early detection of Research Topics
On 2nd of August 2018, I have been invited by Boris Veytsman, Principal Research Scientist at Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (formerly Meta), to give a talk about my PhD work. Differently from my previous talk to the ORNL group, I had the opportunity to describe my doctoral work more comprehensively. More specifically, I initially showed what is available […]

Classifying Research Papers with the Computer Science Ontology
The CSO Classifier is an application for automatically classifying academic papers according to the rich taxonomy of topics from CSO. The aim is to facilitate the adoption of CSO across the various communities engaged with scholarly data and to foster the development of new applications based on this knowledge base.
Springer Nature Hack Day – Berlin
On 26-27 April 2018, Francesco Osborne and I attended the third edition of the Springer Nature Hack Day, which was held in its headquarter in Berlin. The Springer Nature Hack Day is an event that allows researchers, developers, tech companies, and Springer Nature itself, to gather together and tackle current research issues. Offering also opportunities […]

Supporting Editorial Activities at Springer Nature
The project aims at fostering Springer Nature editorial activities by supporting them with a variety of smart solutions leveraging artificial intelligence, data mining, and semantic technologies. In particular, the KMi team will support Springer Nature editorial team in classifying proceedings and other editorial products, taking informed decisions about their marketing strategy, and improve their internal classification.
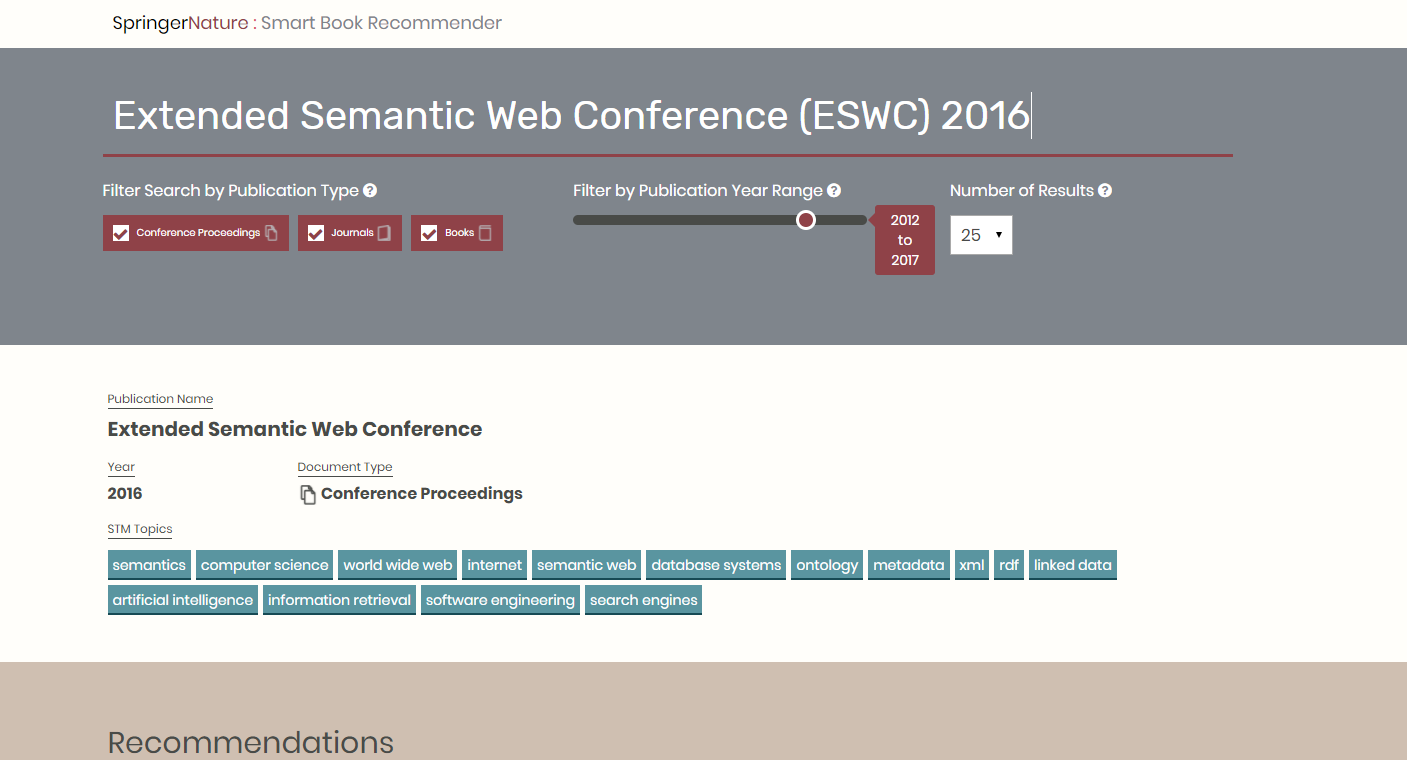
Smart Book Recommender
The Smart Book Recommender (SBR) is a semantic application designed to support the Springer Nature editorial team in promoting their publications at Computer Science venues. It takes as input the proceedings of a conference and suggests books, journals, and other conference proceedings that are likely to be relevant to the attendees of the conference in question. It […]